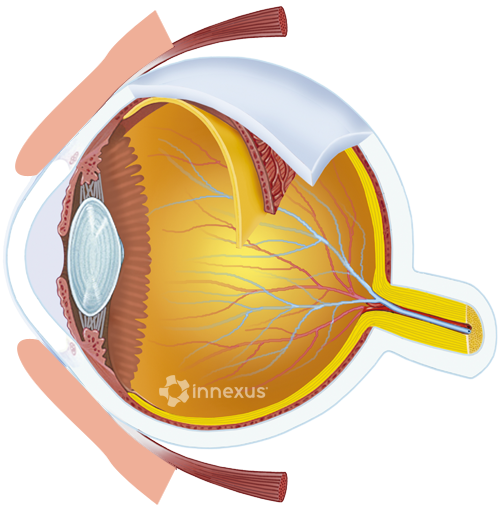









Upper and lower muscular folds of skin that move to cover and uncover the eyeball. |
Transparent front layer of the eye that covers the iris and the pupil. Provides most of the eye's optical power. |
Flat, circular membrane forming the colored portion of the eye, with an adjustable circular opening, the pupil, in the center. |
Dark, circular opening in the center of the iris which varies in size to regulate the amount of light reaching the retina. |
Transparent, biconvex tissue that helps bring rays of light to focus on the retina. |
Small depression in the retina where visual acuity is highest. |
Irregularly oval, yellow-pigmented area on the central retina that contains color-sensitive rods and the region sharpest vision acuity. |
Cell layers, sensitive to light, receive images produced by the lens and triggers nerve impulses that pass via the optic nerve to the brain. |
Pair or cranial nerves, consisting of sensory fibers that transmit sight impulses to the brain. |
Transparent, gelatinous mass which fills two-thirds of the eye between the lens and the retina. |






Follow Us!